
SERIOUS ABOUT BUILDING IN WEB3?
If you're working on something real — let's talk.
Published On Jun 19, 2025
Updated On Feb 16, 2026
Blockchain scalability remains a critical challenge in 2026, as demand for faster, cheaper, and more efficient decentralised applications (dApps) continues to surge.
Layer 1 networks alone can’t keep pace with this growth, highlighting the necessity of Layer 2 solutions.
Rollups have emerged as the leading Layer 2 innovation, compressing transactions off-chain while maintaining the robust security of Layer 1.
Today, Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) is transforming the landscape again, lowering barriers and enabling projects of all sizes to deploy their rollups quickly and securely.
In this blog, we’ll explore how rollups work, the different types available, their technical architecture, a comparison of popular rollup stacks, and key industry trends shaping the future of blockchain scalability.
Let’s get started.
Rollups are Layer 2 solutions designed to solve blockchain’s scalability issues by moving most transaction processing off-chain.
Multiple transactions are bundled together and then submitted to Layer 1 in a single batch, accompanied by proofs or transaction data, depending on the rollup type.
This significantly reduces congestion and transaction costs while leveraging the secure and decentralised nature of Layer 1.
By bundling transactions off-chain and securing them on Layer 1, there are different rollup types that offer tailored solutions balancing scalability and security.
There are different types of rollups, each with its own approach to scaling and securing. Here are the two main categories of rollups powering blockchain scalability today:
Optimistic rollups assume transactions are valid by default and post complete transaction data to Layer 1. They incorporate fraud-proof mechanisms, allowing challenges during a specified window.
Advantages
Examples: Optimism, Arbitrum
Zk-rollups utilise cryptographic proofs (zk-SNARKs/zk-STARKs) to ensure transaction validity instantly, eliminating the need for challenge periods.
Advantages
Examples: zkSync, StarkNet, Loopring
Grasping these distinctions in rollup types sets the stage to dive deeper into the technical architecture behind rollups, about how their components work together to deliver fast, secure, and efficient transaction processing.
Let’s see the architecture behind it.
To truly appreciate how rollups scale blockchain networks, it’s essential to understand their technical architecture and the building blocks that enable Layer 2 scaling.
Here are the core functions that make rollups effective:
This layered approach allows rollups to offload heavy computation and data storage, drastically improving throughput while leveraging Layer 1’s security.
Let’s break down the essential pieces that form the rollup architecture:
These are where smart contracts and transactions run off-chain. Common execution environments include:
This component ensures that transaction data is accessible and verifiable by anyone. Popular options include:
A rollup’s infrastructure connects the technical backbone with real users. Here’s what makes smooth transactions and interaction possible:
Rollup architecture influences how projects select rollup stacks, each optimising speed, security, and flexibility differently.
Knowing these differences helps compare and choose the best fit for your needs.
With the rise of Rollup-as-a-Service, choosing the right rollup stack has become critical.
Different rollup frameworks come with unique strengths, architectures, and deployment options tailored to varied use cases.
Here’s a comparative overview of some of the most prominent rollup stacks in the ecosystem today:
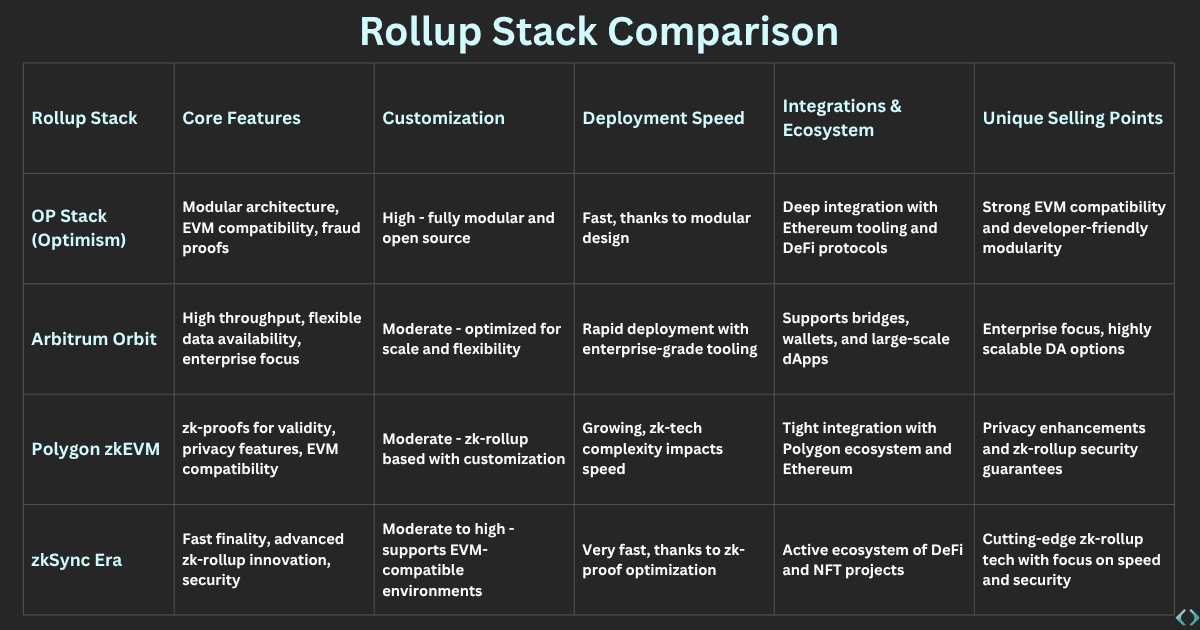
These comparisons emphasise the growing importance of modularity and customisation in rollup technology, helping projects build scalable and adaptable solutions.
With this foundation, it’s important to explore the key industry trends and insights driving the evolution and future of rollups.
One of the biggest breakthroughs Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) brings to blockchain scalability is modularity combined with deep customisation.
This flexibility empowers projects to build rollups perfectly tailored to their unique needs without reinventing the wheel every time.
Whether it’s the execution environment, data availability layer, or transaction sequencing, each part can be selected, upgraded, or replaced independently.
Advantages
Zk-rollups are scaling rapidly by efficiently moving computation off-chain and posting compact proofs on-chain, enabling thousands of transactions per second while drastically lowering gas fees compared to Layer 1.
Their near-instant finality enhances user experience, driving strong adoption with networks like zkSync surpassing 1 million active users.
Universal bridges, such as Hop Protocol and LayerZero, are pioneering this space by enabling fast, secure, and cost-effective transfer of assets and data across disparate chains.
This interoperability reduces friction for users and developers, fostering a truly connected multi-chain environment.
These trends highlight how rollups are boosting scalability, privacy, and interoperability across blockchains.
As the technology matures, its real-world applications grow, leading us to explore the key use cases where rollups are making a difference.
These examples show how rollups boost security and efficiency across industries. If you’re ready to launch your own rollup, here’s the essential toolkit to help you get started.
Rollup deployment is streamlined by resources such as:
Utilising these resources simplifies rollup implementation, enabling quicker market entry.
Rollups and Rollup-as-a-Service are rapidly becoming foundational for blockchain scalability, privacy, interoperability, and enterprise adoption.
As technology advances, modular and zk-rollups will lead the next generation of blockchain innovation, delivering unparalleled speed, security, and adaptability.
To learn how to build and deploy your own secure rollup, check out our comprehensive guide with practical insights and expert tips.

Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) is a development model that helps teams launch Layer 2 rollups quickly by providing modular infrastructure, security tooling, and pre-built components. It simplifies deployment, reduces time-to-market, and supports custom configurations tailored to specific use cases.

The two leading types are Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups. Optimistic Rollups offer EVM compatibility, while zk-Rollups use cryptographic proofs for instant finality and lower fees.

Rollups batch transactions off-chain and post compressed data to Layer 1. This reduces gas fees, increases throughput, and maintains Ethereum-grade security.

Core components include execution environments (EVM or WASM), data availability layers, sequencers, bridges, and RPC nodes. These ensure fast, secure, and reliable Layer 2 operation.

They offer flexibility, speed, and privacy. Teams can customize components, reduce costs, and scale dApps more efficiently across ecosystems.
Need expert guidance on launching your own rollup?
Get personalised consultation for future-proof blockchain solutions.
Talk to our experts